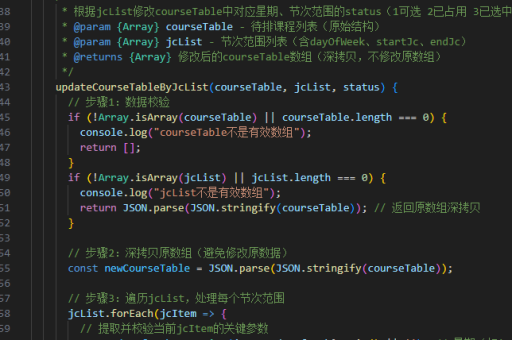
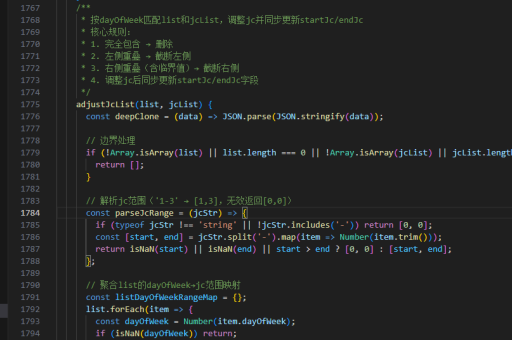
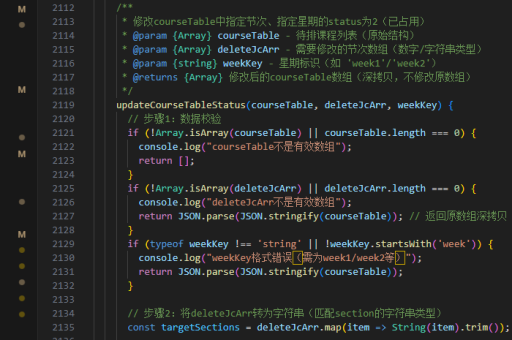
js实现orderby
在JavaScript中实现类似SQL的ORDER BY功能,可以通过数组的sort()方法结合自定义排序逻辑完成。以下是几种常见的实现方式:
基础排序(单字段)
对数组对象按指定属性升序或降序排列:

const data = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 25 },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 30 },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 20 }
];
// 按age升序
data.sort((a, b) => a.age - b.age);
// 按age降序
data.sort((a, b) => b.age - a.age);多字段排序
通过优先级组合多个排序条件:
const data = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 25, score: 80 },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 30, score: 90 },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 20, score: 80 }
];
// 先按score降序,再按age升序
data.sort((a, b) => {
if (a.score !== b.score) {
return b.score - a.score;
}
return a.age - b.age;
});动态排序函数
封装可复用的排序函数,支持动态指定排序字段和方向:
function orderBy(array, fields, directions = []) {
return array.sort((a, b) => {
for (let i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
const field = fields[i];
const direction = directions[i] === 'desc' ? -1 : 1;
if (a[field] < b[field]) return -1 * direction;
if (a[field] > b[field]) return 1 * direction;
}
return 0;
});
}
// 使用示例
const sortedData = orderBy(
data,
['score', 'age'],
['desc', 'asc']
);字符串排序
对字符串属性使用localeCompare实现更精确的排序:
const data = [
{ name: 'Alice', country: 'USA' },
{ name: 'Bob', country: 'Canada' },
{ name: 'Charlie', country: 'UK' }
];
// 按country字段字母顺序排序
data.sort((a, b) => a.country.localeCompare(b.country));注意事项
- 原始数组会被修改,如需保留原数组需先拷贝:
[...array].sort() - 对于可能包含
undefined或null的值,需要额外处理边界情况 - 大数组排序可能影响性能,考虑使用Web Worker或分页处理