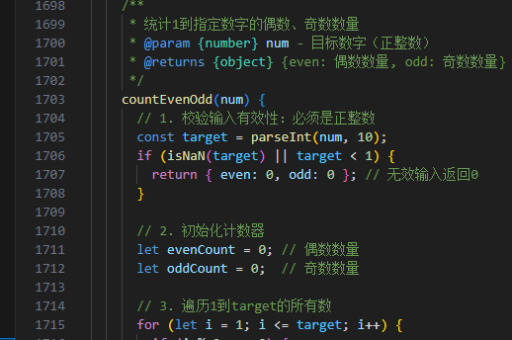
js实现升序
使用数组的 sort 方法实现升序
在 JavaScript 中,数组的 sort 方法默认按照字符串 Unicode 码点排序。若需对数字数组升序排序,需传入比较函数:
const numbers = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6];
numbers.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(numbers); // 输出: [1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9]比较函数 (a, b) => a - b 返回负数时 a 排在 b 前,实现升序排列。
对对象数组按属性升序排序
若需根据对象属性排序,可在比较函数中访问属性值:
const items = [
{ name: 'Apple', price: 50 },
{ name: 'Banana', price: 30 },
{ name: 'Orange', price: 40 }
];
items.sort((a, b) => a.price - b.price);
console.log(items);
// 输出: [
// { name: 'Banana', price: 30 },
// { name: 'Orange', price: 40 },
// { name: 'Apple', price: 50 }
// ]实现字符串数组的升序排序
字符串数组可直接调用 sort() 方法,默认按字典序升序排列:
const fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'orange', 'grape'];
fruits.sort();
console.log(fruits); // 输出: ['apple', 'banana', 'grape', 'orange']自定义复杂排序逻辑
对于需要多条件排序的场景,可在比较函数中扩展逻辑:
const users = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 25, score: 80 },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 30, score: 90 },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 25, score: 85 }
];
users.sort((a, b) => {
if (a.age !== b.age) return a.age - b.age; // 年龄升序
return b.score - a.score; // 同年龄时分数降序
});
console.log(users);
// 输出: [
// { name: 'Alice', age: 25, score: 80 },
// { name: 'Charlie', age: 25, score: 85 },
// { name: 'Bob', age: 30, score: 90 }
// ]注意事项
-
sort方法会修改原数组,若需保留原数组应先创建副本:const original = [3, 1, 4]; const sorted = [...original].sort((a, b) => a - b); -
大数组排序可能影响性能,对于超过 10 万条数据建议考虑专用算法库。
-
比较函数应始终返回数值类型,避免返回布尔值:
- 正确:
(a, b) => a.key - b.key - 错误:
(a, b) => a.key > b.key
- 正确: