vue响应式怎么实现
Vue 响应式实现原理
Vue 的响应式系统通过 数据劫持 和 依赖收集 实现,核心基于 Object.defineProperty(Vue 2)或 Proxy(Vue 3)。以下是具体实现机制:
数据劫持
Vue 2 使用 Object.defineProperty 拦截对象的属性访问和修改,Vue 3 改用 Proxy 代理整个对象,覆盖更多操作(如数组方法、新增属性)。

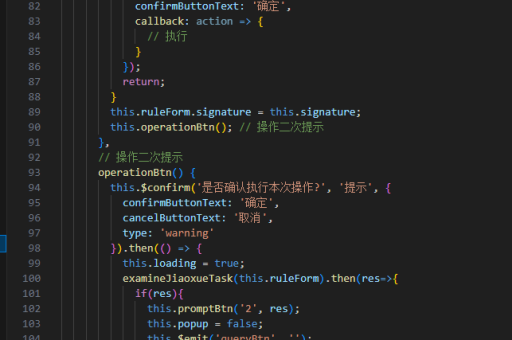
Vue 2 示例:
function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
console.log(`读取 ${key}`);
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
console.log(`更新 ${key}`);
val = newVal;
}
});
}Vue 3 示例:
const reactive = (target) => {
return new Proxy(target, {
get(target, key) {
console.log(`读取 ${key}`);
return Reflect.get(target, key);
},
set(target, key, value) {
console.log(`更新 ${key}`);
return Reflect.set(target, key, value);
}
});
};依赖收集与派发更新
- 依赖收集:在属性被访问时(
getter),将当前执行的组件渲染函数或计算属性作为依赖存入“订阅者列表”。 - 派发更新:属性被修改时(
setter),通知所有订阅者重新执行(如触发组件重新渲染)。
简化实现:
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subscribers = new Set();
}
depend() {
if (activeEffect) this.subscribers.add(activeEffect);
}
notify() {
this.subscribers.forEach(effect => effect());
}
}
let activeEffect = null;
function watchEffect(effect) {
activeEffect = effect;
effect(); // 首次执行触发依赖收集
activeEffect = null;
}数组响应式处理
Vue 2 通过重写数组的变异方法(如 push、pop)实现响应式,本质是拦截方法调用后手动触发更新。
const arrayProto = Array.prototype;
const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto);
['push', 'pop', 'shift'].forEach(method => {
const original = arrayProto[method];
arrayMethods[method] = function(...args) {
const result = original.apply(this, args);
console.log(`数组方法 ${method} 被调用`);
dep.notify(); // 触发更新
return result;
};
});响应式 API 对比
| 特性 | Vue 2 (Object.defineProperty) |
Vue 3 (Proxy) |
|---|---|---|
| 对象新增属性 | 需手动调用 Vue.set |
自动支持 |
| 数组响应式 | 重写变异方法 | 直接拦截 |
| 性能 | 递归遍历对象属性 | 惰性劫持 |
注意事项
- Vue 2 限制:无法检测到对象属性的添加或删除,需通过
Vue.set或Vue.delete处理。 - Vue 3 优势:
Proxy支持深层响应式,且能拦截更多操作(如in操作符、deleteProperty)。
通过上述机制,Vue 实现了数据变化到视图更新的自动化绑定。