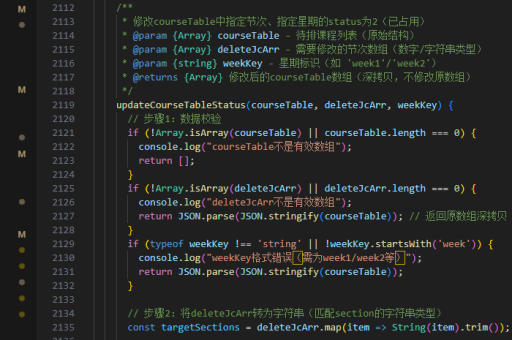
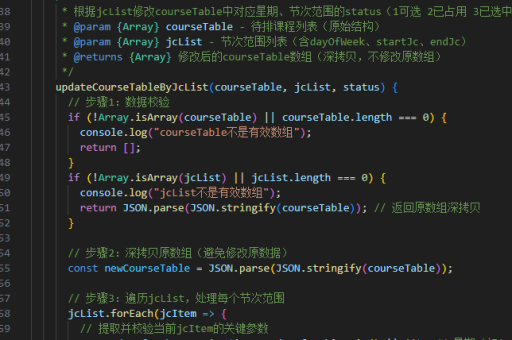
实现vue组件
Vue 组件的基本实现
Vue 组件是 Vue.js 的核心特性之一,允许将 UI 拆分为独立、可复用的模块。以下是实现 Vue 组件的几种方式:
单文件组件 (SFC)
使用 .vue 文件格式,包含模板、脚本和样式:
<template>
<div class="example">{{ msg }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello Vue!'
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.example {
color: red;
}
</style>全局注册组件
通过 Vue.component() 全局注册:
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
})局部注册组件
在父组件中通过 components 选项注册:
const ChildComponent = {
template: '<div>Child Component</div>'
}
new Vue({
components: {
'child-component': ChildComponent
}
})组件通信方式
Props 向下传递数据
父组件通过 props 向子组件传递数据:
<template>
<child-component :message="parentMsg"></child-component>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
parentMsg: 'Message from parent'
}
}
}
</script>子组件接收 props:
export default {
props: ['message']
}自定义事件向上通信
子组件通过 $emit 触发事件:
this.$emit('event-name', payload)父组件监听事件:
<child-component @event-name="handleEvent"></child-component>使用 Provide/Inject
祖先组件提供数据:
provide() {
return {
sharedData: this.sharedValue
}
}后代组件注入数据:
inject: ['sharedData']生命周期钩子
Vue 组件提供多个生命周期钩子:
export default {
created() {
// 实例创建后调用
},
mounted() {
// DOM 挂载后调用
},
updated() {
// 数据更新导致 DOM 重新渲染后调用
},
destroyed() {
// 实例销毁后调用
}
}插槽内容分发
使用插槽实现内容分发:
<template>
<div class="container">
<slot></slot>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>
</template>使用时:
<my-component>
<p>Default slot content</p>
<template v-slot:footer>
<p>Footer content</p>
</template>
</my-component>动态组件
通过 <component> 元素动态切换组件:
<component :is="currentComponent"></component>异步组件
实现按需加载组件:
const AsyncComponent = () => ({
component: import('./MyComponent.vue'),
loading: LoadingComponent,
error: ErrorComponent,
delay: 200,
timeout: 3000
})组件最佳实践
- 保持组件单一职责
- 合理划分组件粒度
- 使用有意义的命名
- 为 props 定义验证规则
- 避免直接修改 props
- 使用 scoped CSS 避免样式冲突
通过以上方式可以构建灵活、可维护的 Vue 组件系统。根据具体场景选择合适的实现方式,组合使用各种通信机制,能够创建出高效的前端应用架构。