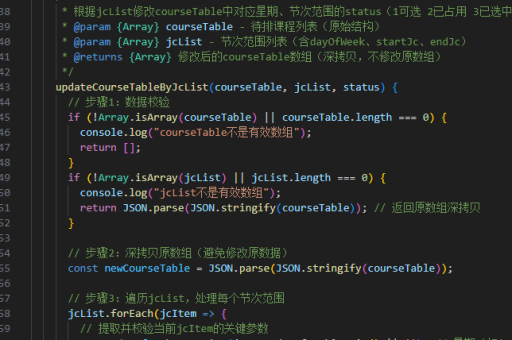
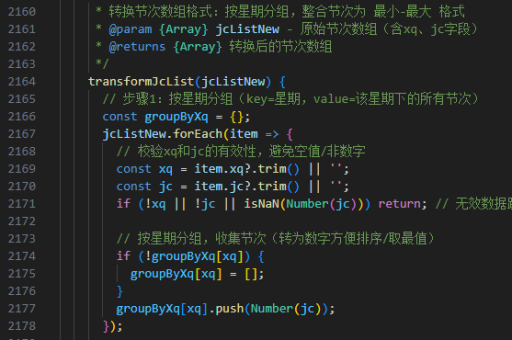
从0实现vue
实现 Vue 的核心功能
Vue 的核心功能包括数据响应式、虚拟 DOM、模板编译等。以下是从零实现 Vue 的基本步骤。
数据响应式系统
数据响应式是 Vue 的核心特性之一,通过 Object.defineProperty 或 Proxy 实现数据劫持。以下是基于 Object.defineProperty 的简单实现:

class Observer {
constructor(data) {
this.walk(data);
}
walk(data) {
if (!data || typeof data !== 'object') return;
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key]);
});
}
defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
const dep = new Dep();
this.walk(val); // 递归处理嵌套对象
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target); // 收集依赖
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) return;
val = newVal;
dep.notify(); // 通知更新
}
});
}
}
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subs = [];
}
addSub(sub) {
this.subs.push(sub);
}
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => sub.update());
}
}
Dep.target = null; // 全局唯一的 Watcher 目标虚拟 DOM 与 Diff 算法
虚拟 DOM 是 Vue 高效更新的关键。以下是虚拟 DOM 的简单实现和 Diff 算法:

class VNode {
constructor(tag, data, children, text, elm) {
this.tag = tag;
this.data = data;
this.children = children;
this.text = text;
this.elm = elm;
}
}
function createElement(tag, data, children) {
return new VNode(tag, data, children, undefined, undefined);
}
function patch(oldVnode, vnode) {
if (!oldVnode) {
// 初次渲染
createElm(vnode);
} else {
// 更新
const isRealElement = oldVnode.nodeType !== undefined;
if (isRealElement) {
// 挂载到真实 DOM
const parent = oldVnode.parentNode;
const refElm = oldVnode.nextSibling;
parent.removeChild(oldVnode);
createElm(vnode, parent, refElm);
} else {
// Diff 更新
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode);
}
}
return vnode.elm;
}
function patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode) {
// 简化版 Diff 逻辑
if (oldVnode === vnode) return;
const elm = (vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm);
const oldCh = oldVnode.children;
const ch = vnode.children;
if (!vnode.text) {
if (oldCh && ch) {
updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch);
} else if (ch) {
// 新增子节点
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1);
} else if (oldCh) {
// 删除子节点
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1);
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
elm.textContent = vnode.text;
}
}模板编译
Vue 的模板编译将模板字符串转换为渲染函数。以下是简化的编译过程:
function compile(template) {
const ast = parse(template); // 解析为 AST
optimize(ast); // 静态节点标记
const code = generate(ast); // 生成渲染函数代码
return new Function(`with(this){return ${code}}`);
}
function parse(template) {
// 简化版解析逻辑
const stack = [];
let root, currentParent;
parseHTML(template, {
start(tag, attrs) {
const element = { tag, attrs, children: [] };
if (!root) root = element;
if (currentParent) currentParent.children.push(element);
stack.push(element);
currentParent = element;
},
end() {
stack.pop();
currentParent = stack[stack.length - 1];
},
chars(text) {
currentParent.children.push({ text });
}
});
return root;
}
function generate(ast) {
return `_c('${ast.tag}',${genData(ast.attrs)},${genChildren(ast.children)})`;
}整合为 Mini-Vue
将以上模块整合为一个简单的 Vue 类:
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options;
this._data = options.data;
new Observer(this._data);
this.$mount(options.el);
}
$mount(el) {
const vm = this;
const { render, template } = vm.$options;
if (!render) {
let template = vm.$options.template;
if (!template && el) {
template = document.querySelector(el).outerHTML;
}
vm.$options.render = compile(template);
}
new Watcher(vm, () => {
const vnode = vm.$options.render.call(vm);
patch(vm._vnode, vnode);
vm._vnode = vnode;
});
}
}
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, fn) {
this.vm = vm;
this.getter = fn;
this.get();
}
get() {
Dep.target = this;
this.getter();
Dep.target = null;
}
update() {
this.get();
}
}使用示例
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Mini-Vue!'
},
template: '<div>{{ message }}</div>'
});以上代码实现了 Vue 的核心功能,包括数据响应式、虚拟 DOM 和模板编译。实际 Vue 的实现更加复杂,包含组件系统、指令、生命周期等更多功能。