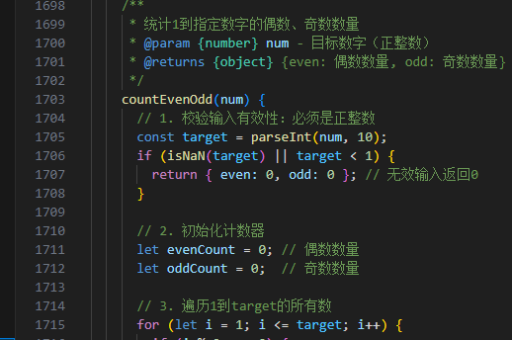
js类实现
使用类实现 JavaScript 功能
在 JavaScript 中,类(Class)是一种语法糖,基于原型继承机制。通过 class 关键字可以更直观地定义对象模板。
基本类定义
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
greet() {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name} and I am ${this.age} years old.`);
}
}
const person = new Person("Alice", 25);
person.greet(); // 输出: Hello, my name is Alice and I am 25 years old.继承与 super
子类可以通过 extends 继承父类,并使用 super 调用父类构造函数或方法。

class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, age, grade) {
super(name, age);
this.grade = grade;
}
study() {
console.log(`${this.name} is studying in grade ${this.grade}.`);
}
}
const student = new Student("Bob", 18, 12);
student.greet(); // 输出: Hello, my name is Bob and I am 18 years old.
student.study(); // 输出: Bob is studying in grade 12.静态方法
静态方法属于类本身,而非实例。
class MathUtils {
static square(x) {
return x * x;
}
}
console.log(MathUtils.square(5)); // 输出: 25Getter 和 Setter
可以使用 get 和 set 定义访问器属性。

class Circle {
constructor(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
get area() {
return Math.PI * this.radius 2;
}
set diameter(d) {
this.radius = d / 2;
}
}
const circle = new Circle(5);
console.log(circle.area); // 输出: ~78.54
circle.diameter = 10;
console.log(circle.radius); // 输出: 5私有字段(ES2022+)
使用 # 前缀定义私有字段,只能在类内部访问。
class Counter {
#count = 0;
increment() {
this.#count++;
}
getCount() {
return this.#count;
}
}
const counter = new Counter();
counter.increment();
console.log(counter.getCount()); // 输出: 1
// console.log(counter.#count); // 报错: 私有字段无法外部访问类表达式
类可以像函数一样通过表达式定义。
const Animal = class {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
speak() {
console.log(`${this.name} makes a noise.`);
}
};
const dog = new Animal("Dog");
dog.speak(); // 输出: Dog makes a noise.通过以上方法,可以灵活运用 JavaScript 类实现面向对象编程。