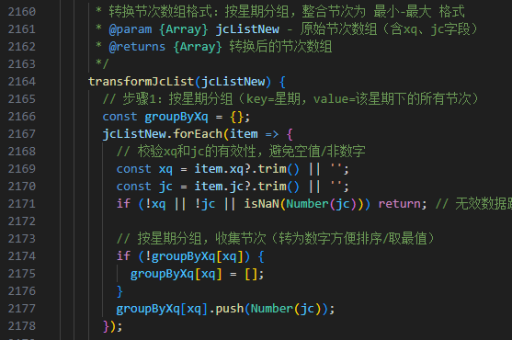
vue组件的实现原理
Vue 组件的实现原理
Vue 组件的核心实现依赖于以下几个关键机制:响应式数据、虚拟 DOM、模板编译和生命周期钩子。
响应式数据
Vue 使用 Object.defineProperty(Vue 2)或 Proxy(Vue 3)实现数据的响应式。当组件的数据发生变化时,Vue 能够自动检测并触发视图更新。例如:
// Vue 2 响应式实现
function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
val = newVal;
// 触发视图更新
}
});
}虚拟 DOM
Vue 通过虚拟 DOM 优化渲染性能。组件的数据变化会生成新的虚拟 DOM 树,通过 Diff 算法对比新旧树,仅更新必要的 DOM 节点。
// 虚拟 DOM 示例
const vnode = {
tag: 'div',
props: { class: 'container' },
children: [
{ tag: 'p', text: 'Hello Vue' }
]
};模板编译
Vue 将模板编译为渲染函数。模板中的指令(如 v-if、v-for)会被转换为 JavaScript 代码,最终生成虚拟 DOM。
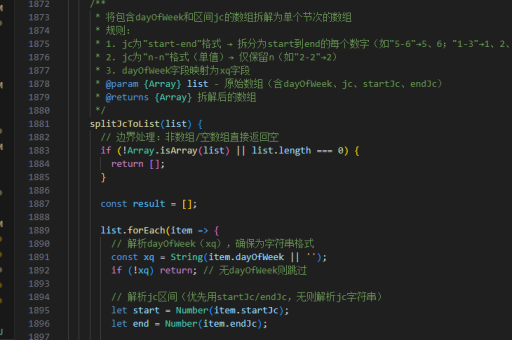
// 模板编译结果示例
function render() {
return h('div', { class: 'container' }, [
h('p', 'Hello Vue')
]);
}生命周期钩子
组件从创建到销毁会触发一系列生命周期钩子(如 created、mounted),开发者可以在这些钩子中执行自定义逻辑。
export default {
created() {
console.log('组件已创建');
},
mounted() {
console.log('组件已挂载');
}
};组件通信机制
Vue 组件通信主要通过 props、events、provide/inject 和 Vuex/Pinia 实现。

Props 和 Events
父组件通过 props 向子组件传递数据,子组件通过 $emit 触发事件通知父组件。
// 父组件
<ChildComponent :message="parentMsg" @update="handleUpdate" />
// 子组件
props: ['message'],
methods: {
notifyParent() {
this.$emit('update', newValue);
}
}Provide/Inject
祖先组件通过 provide 提供数据,后代组件通过 inject 获取数据,适合跨层级通信。
// 祖先组件
provide() {
return { theme: 'dark' };
}
// 后代组件
inject: ['theme']异步组件
Vue 支持异步加载组件,通过动态导入或工厂函数实现代码分割。
const AsyncComponent = () => ({
component: import('./AsyncComponent.vue'),
loading: LoadingComponent,
error: ErrorComponent
});总结
Vue 组件的实现基于响应式数据、虚拟 DOM 和模板编译,通过生命周期钩子管理状态,并提供了多种通信方式。这些机制共同保证了组件的高效渲染和灵活复用。