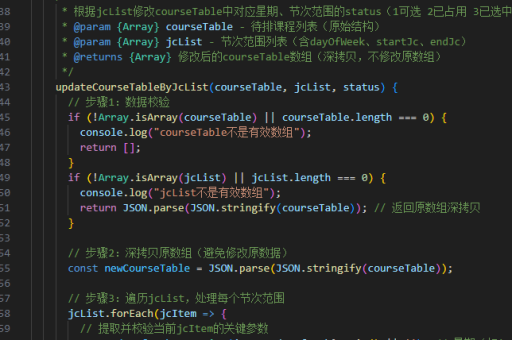
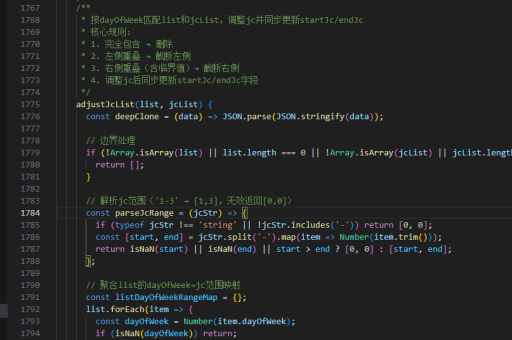
vue中实现异步
异步操作的必要性
在Vue中,异步操作常用于处理API请求、定时任务或文件读取等非阻塞任务,避免界面卡顿并提升用户体验。
使用Promise处理异步
通过Promise封装异步逻辑,结合then/catch或async/await语法简化代码:
methods: {
fetchData() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Data loaded');
}, 1000);
});
},
async loadData() {
try {
const data = await this.fetchData();
console.log(data); // 输出: Data loaded
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
}结合Vue生命周期调用异步
在created或mounted钩子中调用异步方法,确保DOM就绪后处理数据:
created() {
this.loadData(); // 初始化时加载数据
}使用Axios进行HTTP请求
通过Axios库发送异步HTTP请求,处理API响应:
import axios from 'axios';
methods: {
async fetchUser() {
try {
const response = await axios.get('/api/user');
this.user = response.data;
} catch (error) {
console.error('请求失败:', error);
}
}
}处理异步组件加载
使用动态导入实现路由或组件的懒加载,提升应用性能:

const AsyncComponent = () => import('./AsyncComponent.vue');
// 路由配置示例
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [{ path: '/async', component: AsyncComponent }]
});状态管理中的异步操作
在Vuex中通过actions处理异步逻辑,再通过mutations更新状态:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
async fetchData({ commit }) {
const data = await axios.get('/api/data');
commit('SET_DATA', data);
}
},
mutations: {
SET_DATA(state, data) {
state.data = data;
}
}
});错误处理与加载状态
在组件中跟踪异步操作状态,显示加载指示或错误信息:
data() {
return {
isLoading: false,
error: null
};
},
methods: {
async fetchData() {
this.isLoading = true;
try {
await this.$store.dispatch('fetchData');
} catch (err) {
this.error = err.message;
} finally {
this.isLoading = false;
}
}
}注意事项
- 避免在
data中直接存储Promise对象,应处理完成后赋值。 - 使用
async/await时,确保外层函数标记为async。 - 在组件销毁时取消未完成的异步任务(如Axios的CancelToken)。