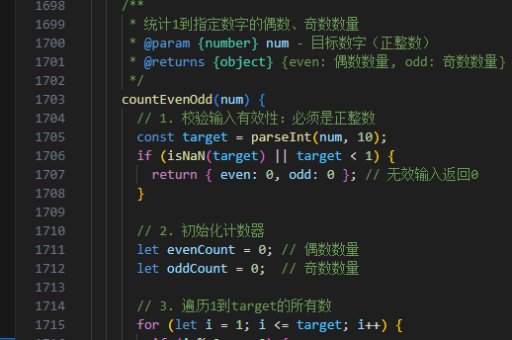
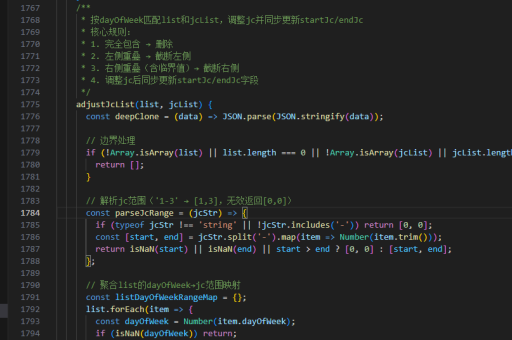
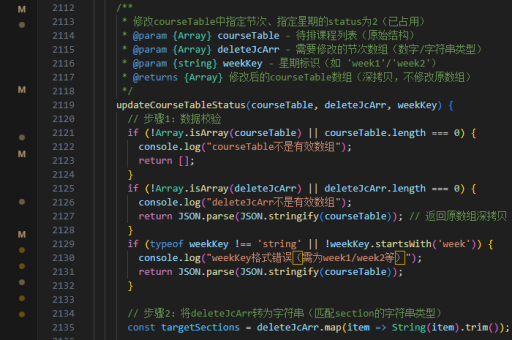
vue实现子页面
Vue 实现子页面的方法
在 Vue 中实现子页面通常可以通过路由嵌套或组件嵌套的方式完成。以下是几种常见的方法:
使用 Vue Router 嵌套路由
通过 Vue Router 的嵌套路由功能,可以轻松实现子页面的层级结构。在路由配置中定义子路由,父组件中通过 <router-view> 渲染子页面。
const routes = [
{
path: '/parent',
component: ParentComponent,
children: [
{
path: 'child',
component: ChildComponent
}
]
}
]在父组件模板中放置 <router-view> 作为子页面的渲染出口:
<template>
<div>
<h1>父页面</h1>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>动态组件切换
通过 Vue 的动态组件 <component :is=""> 实现子页面的切换。这种方式适合不需要路由管理的简单场景。
<template>
<div>
<button @click="currentComponent = 'ChildA'">显示子页面A</button>
<button @click="currentComponent = 'ChildB'">显示子页面B</button>
<component :is="currentComponent"></component>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildA from './ChildA.vue'
import ChildB from './ChildB.vue'
export default {
components: { ChildA, ChildB },
data() {
return {
currentComponent: null
}
}
}
</script>插槽(Slot)方式
使用插槽可以在父组件中预留位置,由父组件决定插入什么子内容。这种方式适合可复用的布局组件。
<!-- ParentComponent.vue -->
<template>
<div class="parent">
<h2>父组件标题</h2>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 使用方式 -->
<parent-component>
<child-component></child-component>
</parent-component>状态管理配合条件渲染
对于复杂应用,可以结合 Vuex 或 Pinia 状态管理,通过条件渲染控制子页面的显示。
<template>
<div>
<ChildA v-if="showChildA" />
<ChildB v-else />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['showChildA'])
}
}
</script>选择建议
- 需要URL导航和浏览器历史记录时,使用Vue Router嵌套路由
- 简单组件切换无需URL变化时,使用动态组件
- 需要灵活的内容插入时,考虑插槽方式
- 复杂状态管理场景下,结合状态库使用条件渲染
每种方法各有适用场景,可根据具体需求选择最合适的实现方式。