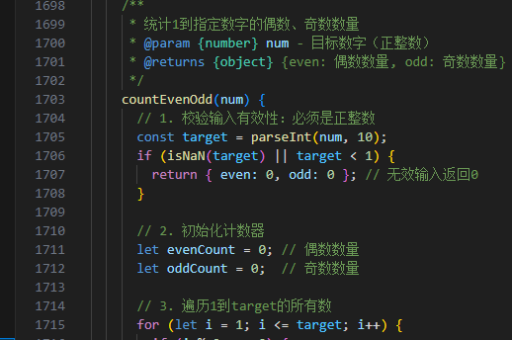
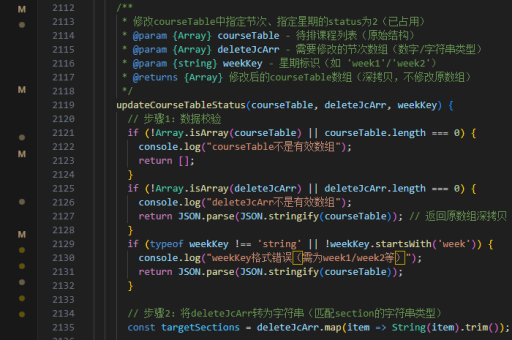
vue缓存实现原理
Vue 缓存实现原理
Vue 中的缓存主要通过 keep-alive 组件实现,用于缓存动态组件或路由组件,避免重复渲染和销毁,提升性能。
keep-alive 的核心机制
keep-alive 是一个抽象组件,不会渲染成真实的 DOM 节点。它通过 include、exclude 和 max 属性控制缓存策略。
- 缓存匹配:通过
include和exclude属性匹配组件名称,决定是否缓存。 - LRU 算法:当缓存数量超过
max时,采用最近最少使用(LRU)策略淘汰最久未访问的组件。
缓存的生命周期钩子
被缓存的组件会触发特定的生命周期钩子:
activated:组件被激活时调用(从缓存中重新插入 DOM)。deactivated:组件被停用时调用(从 DOM 移除,但保留在缓存中)。
实现原理代码片段
keep-alive 的核心逻辑是通过 cache 对象存储组件实例,并通过 keys 数组管理访问顺序:
// 伪代码示例
const cache = Object.create(null)
const keys = []
function pruneCacheEntry(key) {
const cached = cache[key]
if (cached) {
cached.componentInstance.$destroy()
delete cache[key]
keys.splice(keys.indexOf(key), 1)
}
}
function render() {
const slot = this.$slots.default
const vnode = getFirstComponentChild(slot)
const key = vnode.key ?? vnode.componentOptions.Ctor.cid
if (cache[key]) {
vnode.componentInstance = cache[key].componentInstance
// 更新 key 的访问顺序
keys.splice(keys.indexOf(key), 1)
keys.push(key)
} else {
cache[key] = vnode
keys.push(key)
if (this.max && keys.length > this.max) {
pruneCacheEntry(keys[0])
}
}
vnode.data.keepAlive = true
return vnode
}与 Vue Router 的结合
在 Vue Router 中,可以通过 <router-view> 嵌套 <keep-alive> 实现路由级别的缓存:
<keep-alive>
<router-view v-if="$route.meta.keepAlive" />
</keep-alive>
<router-view v-if="!$route.meta.keepAlive" />需在路由配置中通过 meta 字段标记需要缓存的页面:
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
meta: { keepAlive: true }
}性能优化注意事项
- 缓存数量控制:避免无限制缓存,合理设置
max属性。 - 内存管理:及时清理不需要的缓存,防止内存泄漏。
- 动态组件:对于频繁切换的动态组件,缓存能显著减少渲染开销。