vue虚拟滚动实现
vue虚拟滚动实现
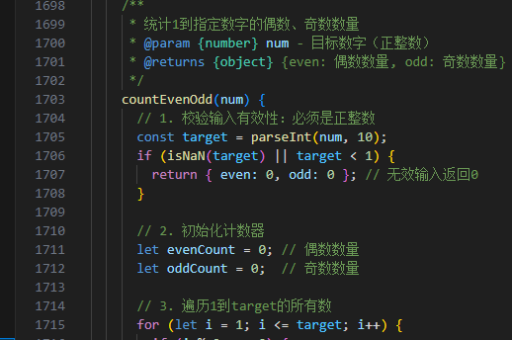
虚拟滚动(Virtual Scrolling)是一种优化长列表渲染性能的技术,通过仅渲染可见区域内的元素来减少DOM节点数量。以下是几种常见的实现方式:
使用第三方库
推荐使用成熟的虚拟滚动库,例如 vue-virtual-scroller 或 vue-virtual-scroll-list。

安装 vue-virtual-scroller:
npm install vue-virtual-scroller基本用法:
<template>
<RecycleScroller
class="scroller"
:items="items"
:item-size="32"
key-field="id"
v-slot="{ item }"
>
<div class="user">
{{ item.name }}
</div>
</RecycleScroller>
</template>
<script>
import { RecycleScroller } from 'vue-virtual-scroller'
import 'vue-virtual-scroller/dist/vue-virtual-scroller.css'
export default {
components: {
RecycleScroller
},
data() {
return {
items: Array.from({ length: 10000 }, (_, i) => ({ id: i, name: `User ${i}` }))
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.scroller {
height: 400px;
}
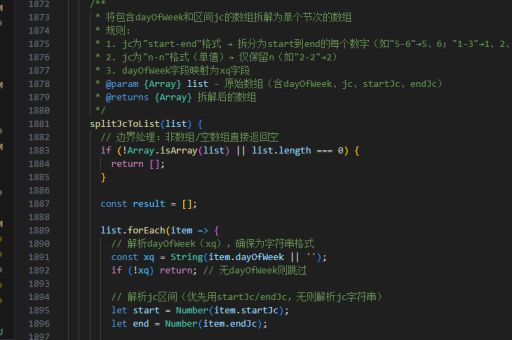
</style>手动实现虚拟滚动
对于需要自定义的场景,可以手动实现虚拟滚动逻辑。
<template>
<div class="virtual-scroll" @scroll="handleScroll" ref="scrollElement">
<div class="scroll-content" :style="{ height: totalHeight + 'px' }">
<div
v-for="item in visibleItems"
:key="item.id"
class="item"
:style="{ transform: `translateY(${item.offset}px)` }"
>
{{ item.content }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
items: Array.from({ length: 10000 }, (_, i) => ({
id: i,
content: `Item ${i}`,
height: 50 // 假设每个项目高度固定
})),
visibleStartIndex: 0,
visibleEndIndex: 0,
scrollTop: 0
}
},
computed: {
totalHeight() {
return this.items.reduce((sum, item) => sum + item.height, 0)
},
visibleItems() {
return this.items
.slice(this.visibleStartIndex, this.visibleEndIndex)
.map(item => ({
...item,
offset: this.items
.slice(0, item.id)
.reduce((sum, i) => sum + i.height, 0)
}))
}
},
mounted() {
this.updateVisibleItems()
},
methods: {
handleScroll() {
this.scrollTop = this.$refs.scrollElement.scrollTop
this.updateVisibleItems()
},
updateVisibleItems() {
const { scrollTop } = this
const viewportHeight = this.$refs.scrollElement.clientHeight
let startIndex = 0
let endIndex = 0
let currentHeight = 0
// 计算可见区域的起始索引
for (let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
if (currentHeight >= scrollTop) {
startIndex = i
break
}
currentHeight += this.items[i].height
}
// 计算可见区域的结束索引
currentHeight = 0
for (let i = startIndex; i < this.items.length; i++) {
if (currentHeight > scrollTop + viewportHeight) {
break
}
endIndex = i
currentHeight += this.items[i].height
}
// 增加缓冲项
const buffer = 5
this.visibleStartIndex = Math.max(0, startIndex - buffer)
this.visibleEndIndex = Math.min(this.items.length - 1, endIndex + buffer)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.virtual-scroll {
height: 500px;
overflow-y: auto;
position: relative;
}
.scroll-content {
position: relative;
}
.item {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border-bottom: 1px solid #eee;
}
</style>动态高度处理
对于高度不固定的项目,需要先测量项目高度:
methods: {
measureItems() {
this.$nextTick(() => {
const nodes = this.$refs.items
nodes.forEach((node, index) => {
this.items[index].height = node.clientHeight
})
})
}
}性能优化技巧
- 使用
requestAnimationFrame节流滚动事件 - 对于固定高度的项目,可以跳过测量步骤
- 合理设置缓冲区域大小,平衡性能与用户体验
- 考虑使用
Object.freeze冻结不需要响应式的数据
以上方法可以根据具体需求选择使用,第三方库通常提供更完善的解决方案,而手动实现则更适合特殊定制场景。