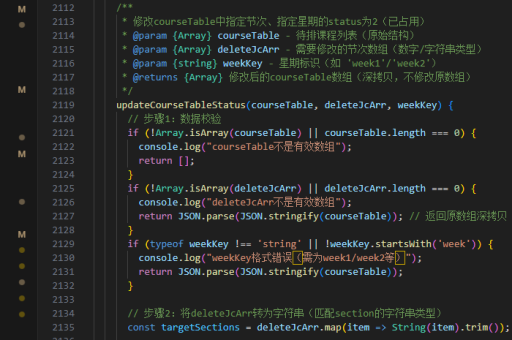
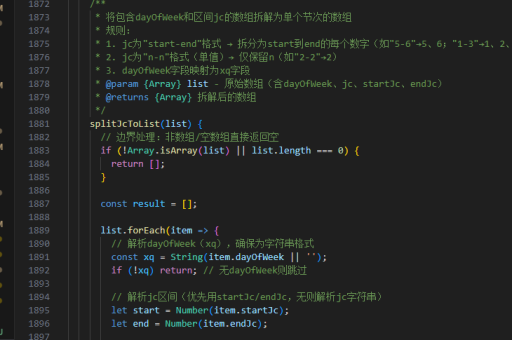
vue mvvm实现
Vue 的 MVVM 实现原理
Vue 是一个基于 MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)设计模式的前端框架,通过数据绑定和响应式系统实现视图与数据的自动同步。以下是 Vue 实现 MVVM 的核心机制:
数据劫持与响应式系统
Vue 使用 Object.defineProperty(Vue 2)或 Proxy(Vue 3)对数据进行劫持,监听数据变化。当数据被修改时,触发依赖更新。

// Vue 2 的数据劫持示例
const data = { name: 'Vue' };
Object.defineProperty(data, 'name', {
get() {
console.log('获取数据');
return this._name;
},
set(newVal) {
console.log('更新数据');
this._name = newVal;
// 触发视图更新
}
});依赖收集与观察者模式
Vue 通过 Dep(依赖管理器)和 Watcher(观察者)实现依赖收集。每个响应式属性都有一个 Dep 实例,用于存储依赖该属性的 Watcher。
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.subscribers = [];
}
depend() {
if (target && !this.subscribers.includes(target)) {
this.subscribers.push(target);
}
}
notify() {
this.subscribers.forEach(sub => sub());
}
}模板编译与虚拟 DOM
Vue 将模板编译为渲染函数,生成虚拟 DOM(VNode)。通过 diff 算法对比新旧 VNode,高效更新真实 DOM。

// 示例:模板编译为渲染函数
const template = '<div>{{ name }}</div>';
const render = new Function('with(this){return _c("div",[_v(_s(name))])}');双向数据绑定
通过 v-model 指令实现双向绑定,本质是语法糖:
- 将
value属性绑定到数据(Model → View)。 - 监听
input事件更新数据(View → Model)。
<input v-model="message">
<!-- 等价于 -->
<input :value="message" @input="message = $event.target.value">实现简易 MVVM 示例
以下是一个简化版的 MVVM 实现:
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
this.$data = options.data;
this.observe(this.$data);
this.compile(options.el);
}
observe(data) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
let value = data[key];
const dep = new Dep();
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
get() {
if (Dep.target) dep.depend();
return value;
},
set(newVal) {
value = newVal;
dep.notify();
}
});
});
}
compile(el) {
const element = document.querySelector(el);
this.compileNode(element);
}
compileNode(node) {
if (node.nodeType === 1) { // 元素节点
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
if (attr.name.startsWith('v-')) {
const dir = attr.name.substring(2);
if (dir === 'model') {
node.value = this.$data[attr.value];
node.addEventListener('input', e => {
this.$data[attr.value] = e.target.value;
});
}
}
});
}
if (node.childNodes) {
node.childNodes.forEach(child => this.compileNode(child));
}
}
}关键点总结
- 数据劫持:通过
Object.defineProperty或Proxy监听数据变化。 - 依赖收集:在 getter 中收集依赖,在 setter 中触发更新。
- 批量异步更新:通过队列机制优化多次数据变更的渲染性能。
- 虚拟 DOM:减少直接操作 DOM 的开销,提升性能。