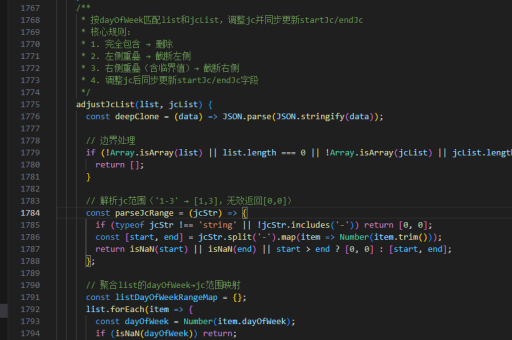
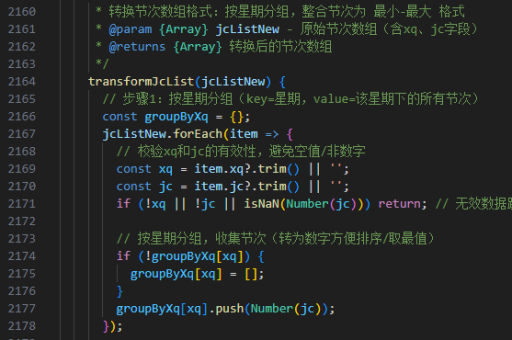
php代码实现跳转
PHP 实现页面跳转的方法
使用 header() 函数实现跳转header() 函数是 PHP 中最常用的跳转方法,通过发送 HTTP 头部信息实现重定向。
确保在调用 header() 之前没有输出任何内容(包括空格和 HTML 标签),否则会触发错误。
跳转后建议使用 exit() 终止脚本执行,避免后续代码继续运行。
header("Location: https://example.com");
exit();延迟跳转的实现
通过 header() 结合 refresh 实现延迟跳转
可以在 HTTP 头部添加 refresh 参数,指定跳转的延迟时间(秒)和目标 URL。
header("Refresh: 3; url=https://example.com");
echo "页面将在 3 秒后跳转...";
exit();使用 HTML 的 meta 标签跳转
如果无法使用 header() 函数(如已有内容输出),可以通过 HTML 的 <meta> 标签实现跳转。
这种方式适用于混合 PHP 和 HTML 的场景。

echo '<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="3;url=https://example.com">';JavaScript 跳转的 PHP 实现
通过输出 JavaScript 代码实现跳转
适用于需要客户端控制的场景,例如条件跳转或动态 URL 生成。
echo '<script>window.location.href = "https://example.com";</script>';跳转时传递参数
在跳转 URL 中附加查询参数
可以通过拼接 URL 字符串传递参数,适用于 GET 请求的场景。

$id = 123;
header("Location: https://example.com/page.php?id=$id");
exit();条件跳转的实现
根据逻辑判断决定跳转目标
结合条件语句实现动态跳转,例如用户权限验证后的跳转。
if ($isAdmin) {
header("Location: /admin.php");
} else {
header("Location: /user.php");
}
exit();跳转时保存会话状态
确保跳转前后会话(Session)保持
使用 session_start() 在跳转前初始化会话,避免会话数据丢失。
session_start();
$_SESSION['user'] = 'John';
header("Location: /profile.php");
exit();