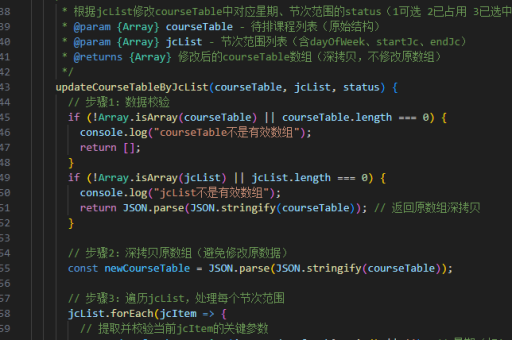
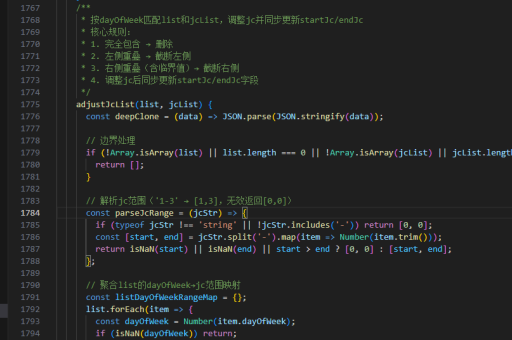
react如何加快编译
优化 Webpack 配置
启用 HardSourceWebpackPlugin 缓存模块构建结果,减少重复编译时间。配置 babel-loader 时排除 node_modules,缩小转译范围。使用 thread-loader 并行处理耗时的加载器任务。
// webpack.config.js
const HardSourceWebpackPlugin = require('hard-source-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.jsx?$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: ['thread-loader', 'babel-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [new HardSourceWebpackPlugin()]
};使用 SWC 替代 Babel
SWC(Speedy Web Compiler)是基于 Rust 的转译工具,比 Babel 快 20 倍以上。通过 @swc/core 和 swc-loader 替换原有 Babel 配置。
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.jsx?$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: 'swc-loader',
options: {
jsc: {
parser: {
syntax: 'ecmascript',
jsx: true
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
};启用增量编译与持久缓存
Webpack 5 内置持久缓存功能,通过 cache 字段配置。结合 filesystem 缓存类型可显著提升二次编译速度。
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
cache: {
type: 'filesystem',
buildDependencies: {
config: [__filename]
}
}
};减少 Polyfill 体积
通过 browserslist 精准定位目标环境,避免不必要的 Polyfill。使用 @babel/preset-env 的 useBuiltIns: 'usage' 按需引入。
// .browserslistrc
last 2 Chrome versions
not IE 11代码分割与动态导入
使用 React 的 lazy 和 Suspense 实现动态加载,减少初始编译负担。配合 Webpack 的 splitChunks 拆分公共依赖。
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));
function App() {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<LazyComponent />
</React.Suspense>
);
}升级依赖版本
确保 React、Webpack 及相关插件为最新稳定版。新版工具链通常包含性能优化,如 Webpack 5 的模块联邦和 Tree Shaking 改进。