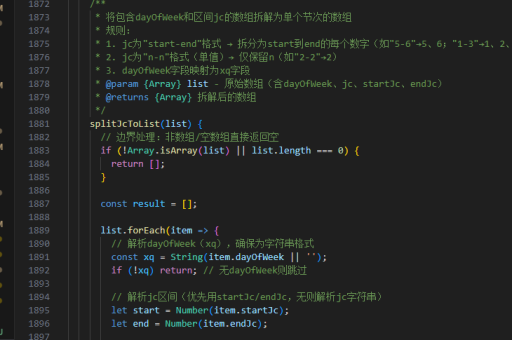
vue递归实现
递归组件的实现方法
在Vue中实现递归组件通常需要组件引用自身,适用于树形结构、嵌套菜单等场景。以下是具体实现方式:
定义递归组件
确保组件拥有name属性,这是递归调用的关键。通过import引入自身并在components中注册:
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ node.label }}</div>
<child-component
v-for="child in node.children"
:key="child.id"
:node="child"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'ChildComponent',
props: {
node: Object
}
}
</script>动态组件递归
通过is特性动态渲染组件,避免循环引用问题:
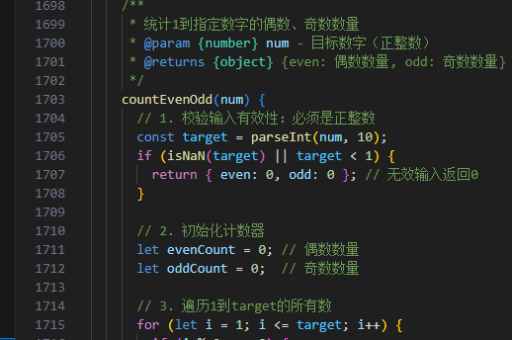
<template>
<component
:is="node.children ? 'ChildComponent' : 'span'"
:node="node"
/>
</template>终止条件处理
递归组件必须包含终止条件,否则会导致无限循环。通过v-if判断子节点是否存在:
<template>
<div>
<div>{{ node.label }}</div>
<child-component
v-if="node.children && node.children.length"
v-for="child in node.children"
:key="child.id"
:node="child"
/>
</div>
</template>性能优化建议
对于深层递归结构,建议采用以下优化措施:
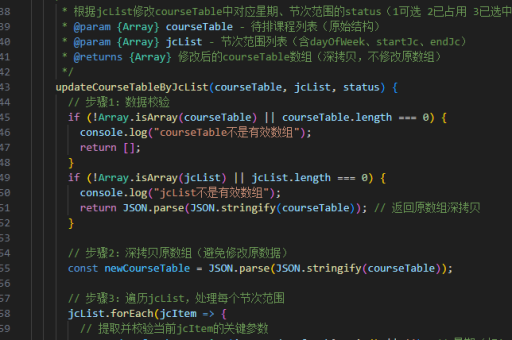
设置递归深度限制
通过maxDepthprop控制递归层级:
props: {
node: Object,
maxDepth: {
type: Number,
default: 5
},
currentDepth: {
type: Number,
default: 0
}
}使用异步加载 对深层节点采用异步加载方式:
methods: {
loadChildren() {
if (this.node.hasChildren && !this.node.children) {
fetchChildren(this.node.id).then(children => {
this.$set(this.node, 'children', children)
})
}
}
}实际应用示例
以下是文件目录树的完整实现示例:
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in treeData" :key="item.path">
{{ item.name }}
<file-tree
v-if="item.children"
:tree-data="item.children"
/>
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'FileTree',
props: {
treeData: {
type: Array,
required: true
}
}
}
</script>注意事项
- 避免在递归组件中使用
v-for和v-if在同一元素上 - 为每个递归项设置唯一的
key属性 - 深层递归可能导致堆栈溢出,建议设置深度阈值
- 在Vue 3中可以使用
<script setup>简化递归组件定义