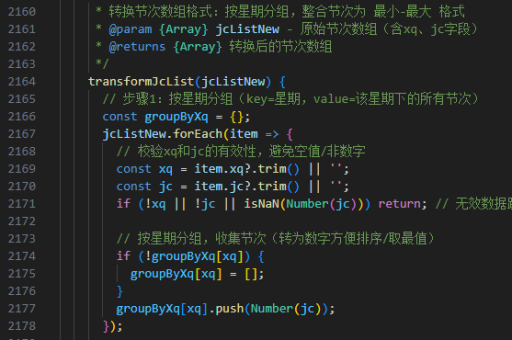
vue工序实现
Vue 工序实现方法
Vue 工序实现通常涉及组件化开发、状态管理、路由配置等核心功能。以下是实现 Vue 工序的常见方法:
组件化开发
创建可复用的 Vue 组件,通过 props 和 events 实现父子组件通信。使用单文件组件(SFC)组织模板、脚本和样式。

<template>
<div>{{ message }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
message: String
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
div {
color: red;
}
</style>状态管理 对于复杂应用,使用 Vuex 或 Pinia 管理全局状态。定义 store、mutations、actions 和 getters 实现数据流管理。
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}
})路由配置
使用 Vue Router 实现页面导航。定义路由表并通过 <router-link> 和 <router-view> 实现路由切换。

import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About }
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes
})API 集成 通过 axios 或 fetch 与后端 API 交互。在组件或 store 中发起异步请求处理数据。
import axios from 'axios'
axios.get('/api/data')
.then(response => {
console.log(response.data)
})生命周期钩子
利用 Vue 的生命周期钩子(如 created、mounted)执行初始化逻辑或清理操作。
export default {
created() {
this.fetchData()
},
methods: {
fetchData() {
// API 调用
}
}
}