java接口如何设计
接口设计原则
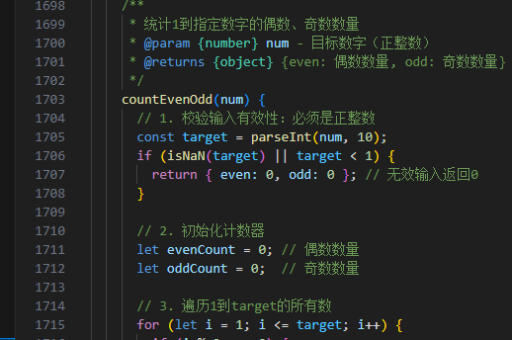
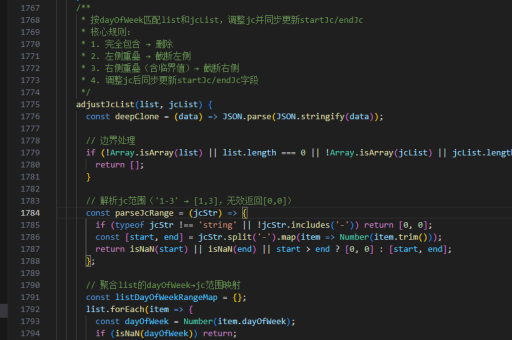
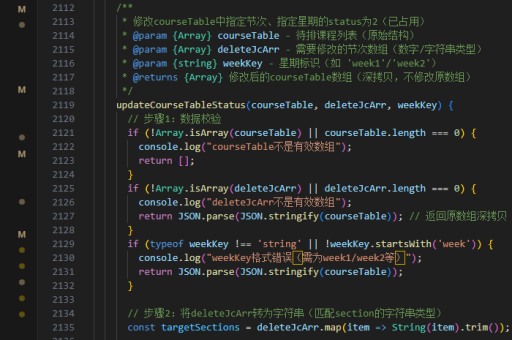
遵循单一职责原则,确保每个接口只定义一个明确的功能或行为。避免设计过于复杂的接口,保持高内聚低耦合。使用interface关键字定义接口,方法默认是public abstract的。
public interface Animal {
void eat();
void sleep();
}默认方法与静态方法
Java 8开始支持接口中使用default和static方法。default方法提供默认实现,避免破坏现有实现类;static方法用于定义工具方法。

public interface Calculator {
default int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
static int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
}接口继承
接口支持多继承,可以通过extends关键字继承多个父接口。子接口会继承所有父接口的抽象方法和默认方法。
public interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
public interface Swimmable {
void swim();
}
public interface Duck extends Flyable, Swimmable {
void quack();
}标记接口
没有定义任何方法的接口称为标记接口,用于标识类的特性。例如Serializable接口仅用于标记类可序列化。

public interface Serializable {
// 无方法定义
}函数式接口
只包含一个抽象方法的接口称为函数式接口,可用@FunctionalInterface注解标注。常用于Lambda表达式和方法引用。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Greeter {
void greet(String name);
}接口与抽象类对比
接口强调行为契约,支持多继承;抽象类强调代码复用,可包含状态。优先使用接口设计,需要共享代码时再考虑抽象类。
// 接口示例
public interface Drawable {
void draw();
}
// 抽象类示例
public abstract class Shape implements Drawable {
protected String color;
public abstract double area();
}