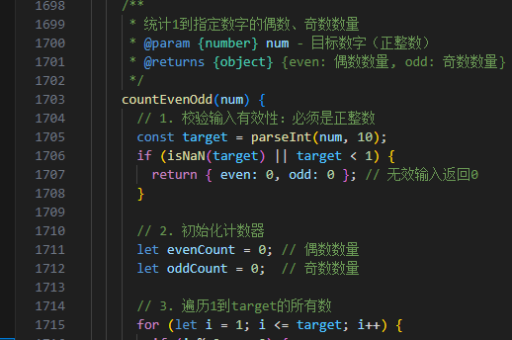
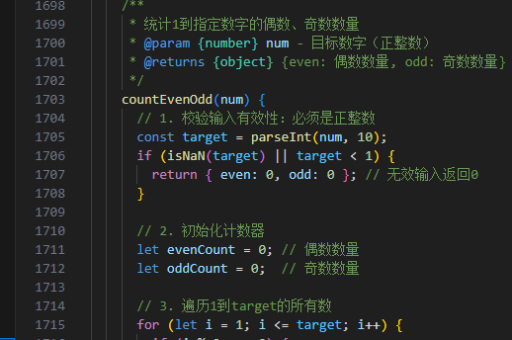
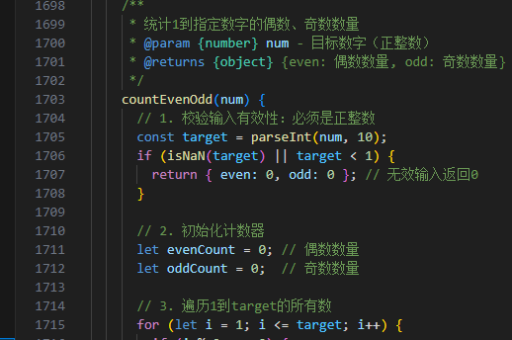
java并发如何处理
Java并发处理的核心方法
Java提供了多种机制处理并发编程,确保线程安全和高效执行。以下是关键方法:
使用synchronized关键字 synchronized可以修饰方法或代码块,确保同一时间只有一个线程执行该代码。适用于简单的同步需求,但可能引发性能问题。
public synchronized void increment() {
count++;
}ReentrantLock类 提供比synchronized更灵活的锁机制,支持公平锁、尝试获取锁和中断等待。
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void method() {
lock.lock();
try {
// 临界区代码
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}并发集合 java.util.concurrent包提供线程安全的集合类,如ConcurrentHashMap、CopyOnWriteArrayList等,替代传统的同步集合。
原子变量 AtomicInteger、AtomicLong等类提供原子操作,无需锁即可实现线程安全。
private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void increment() {
counter.incrementAndGet();
}Executor框架 通过线程池管理线程生命周期,提高性能并降低资源消耗。
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
executor.submit(() -> {
// 任务代码
});
executor.shutdown();CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier 协调多个线程的同步工具。CountDownLatch等待指定数量事件发生,CyclicBarrier让一组线程互相等待到达屏障点。
volatile关键字 确保变量的可见性,但不保证原子性。适用于一个线程写、多个线程读的场景。
CompletableFuture Java 8引入的异步编程工具,支持非阻塞操作和回调。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "result")
.thenApply(s -> s.toUpperCase())
.thenAccept(System.out::println);并发编程最佳实践
避免共享可变状态,优先使用不可变对象和线程局部变量。
最小化同步范围,只锁必要的代码块,减少锁竞争。
考虑使用读写锁(ReentrantReadWriteLock)优化读多写少场景。
优先使用并发工具类而非手动实现同步机制。
注意死锁预防,确保锁的获取顺序一致。
使用ThreadLocal为每个线程维护独立变量副本,避免共享。