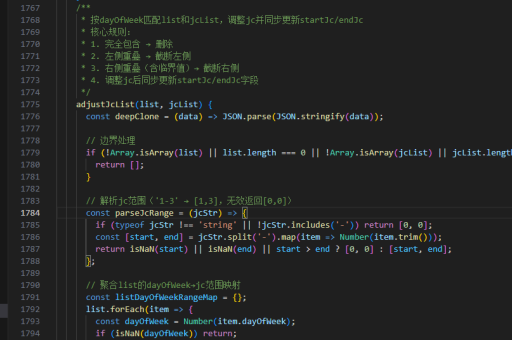
js extends 实现
继承的实现方式
在JavaScript中,继承可以通过多种方式实现。以下是几种常见的继承实现方法:
原型链继承
原型链继承是通过将子类的原型对象指向父类的实例来实现的。子类通过原型链可以访问父类的属性和方法。
function Parent() {
this.name = 'Parent';
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child() {
this.childName = 'Child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
const child = new Child();
child.sayName(); // 输出: Parent构造函数继承
构造函数继承是通过在子类的构造函数中调用父类的构造函数来实现的。这种方式可以避免引用类型的共享问题。
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
const child = new Child('Child', 10);
console.log(child.name); // 输出: Child组合继承
组合继承结合了原型链继承和构造函数继承的优点,既能够继承父类的原型方法,又能够避免引用类型的共享问题。

function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
const child = new Child('Child', 10);
child.sayName(); // 输出: Child原型式继承
原型式继承是通过创建一个临时构造函数来实现的,适用于不需要单独创建构造函数的情况。
const parent = {
name: 'Parent',
sayName: function() {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
const child = Object.create(parent);
child.name = 'Child';
child.sayName(); // 输出: Child寄生式继承
寄生式继承是在原型式继承的基础上增强对象,返回一个增强后的对象。

function createChild(parent) {
const child = Object.create(parent);
child.sayAge = function() {
console.log(this.age);
};
return child;
}
const parent = {
name: 'Parent'
};
const child = createChild(parent);
child.age = 10;
child.sayAge(); // 输出: 10寄生组合式继承
寄生组合式继承是组合继承的优化版本,避免了两次调用父类构造函数的问题。
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
const child = new Child('Child', 10);
child.sayName(); // 输出: ChildES6 Class继承
ES6引入了class和extends关键字,使得继承更加简洁和直观。
class Parent {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
sayName() {
console.log(this.name);
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name);
this.age = age;
}
}
const child = new Child('Child', 10);
child.sayName(); // 输出: Child继承的选择
根据不同的需求选择合适的继承方式:
- 如果需要简单的继承,可以使用原型链继承或ES6的
class和extends。 - 如果需要避免引用类型的共享问题,可以使用构造函数继承或组合继承。
- 如果需要更灵活的继承方式,可以使用原型式继承或寄生式继承。
- 如果需要最优化的继承方式,可以使用寄生组合式继承。
注意事项
- 原型链继承会导致引用类型的属性被所有实例共享。
- 构造函数继承无法继承父类原型上的方法。
- 组合继承会调用两次父类构造函数,可能影响性能。
- ES6的
class和extends语法糖背后仍然是基于原型的继承。