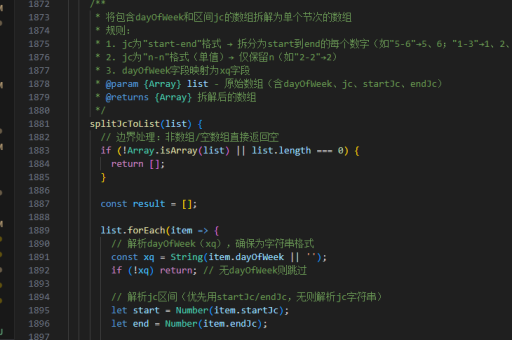
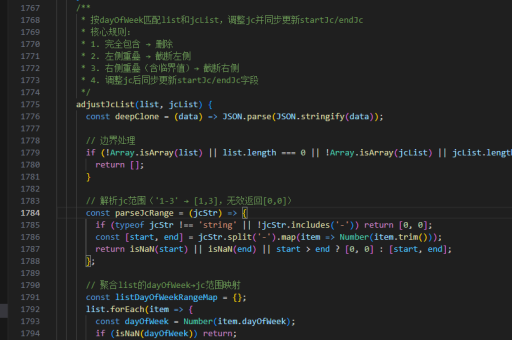
js实现几率
实现随机几率的方法
在JavaScript中实现随机几率可以通过多种方式完成,具体取决于需求场景。以下是几种常见的方法:
Math.random()基础方法
使用Math.random()生成一个0到1之间的随机数,通过判断该随机数是否落在指定范围内实现几率控制:
const probability = 0.3; // 30%几率
if (Math.random() < probability) {
console.log("触发成功");
} else {
console.log("未触发");
}权重随机选择
当需要从多个选项中以不同几率随机选择时,可以使用权重系统:
const options = [
{ item: "A", weight: 0.1 },
{ item: "B", weight: 0.3 },
{ item: "C", weight: 0.6 }
];
function weightedRandom(options) {
const random = Math.random();
let sum = 0;
for (const option of options) {
sum += option.weight;
if (random <= sum) return option.item;
}
return options[options.length-1].item;
}
console.log(weightedRandom(options));正态分布随机
使用Box-Muller变换生成符合正态分布的随机数:
function normalRandom(mean=0, stdev=1) {
const u = 1 - Math.random();
const v = Math.random();
const z = Math.sqrt(-2.0 * Math.log(u)) * Math.cos(2.0 * Math.PI * v);
return z * stdev + mean;
}
console.log(normalRandom(100, 15));实际应用示例
抽奖系统实现
构建一个简单的抽奖系统,不同奖品有不同的中奖几率:
const prizes = [
{ name: "一等奖", chance: 0.01 },
{ name: "二等奖", chance: 0.05 },
{ name: "三等奖", chance: 0.1 },
{ name: "参与奖", chance: 0.84 }
];
function drawPrize(prizes) {
const random = Math.random();
let cumulative = 0;
for (const prize of prizes) {
cumulative += prize.chance;
if (random <= cumulative) return prize.name;
}
return "未中奖";
}
console.log(drawPrize(prizes));游戏暴击率计算
游戏中暴击几率的实现可以结合伪随机分布,避免连续暴击或长期不暴击:
let pseudoRandomCounter = 0;
const baseCritChance = 0.2;
function getCrit() {
pseudoRandomCounter++;
const actualChance = baseCritChance * pseudoRandomCounter;
if (Math.random() < actualChance) {
pseudoRandomCounter = 0;
return true;
}
return false;
}注意事项
- 确保所有几率的和为1(100%),否则可能导致意外结果
- 对于高精度需求,考虑使用更专业的随机数生成库
- 在安全敏感场景避免使用
Math.random(),改用crypto.getRandomValues() - 测试时使用大量样本验证实际分布是否符合预期