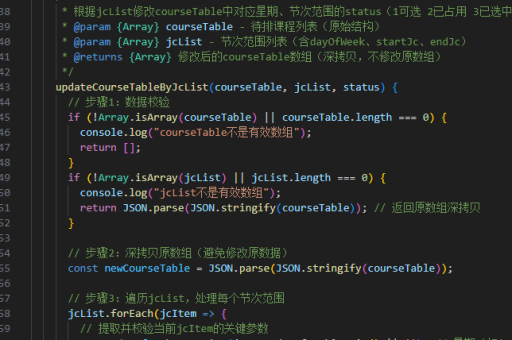
js实现分页代码
分页实现方法
前端分页(纯JavaScript)
适用于数据量较小的情况,直接在客户端完成分页逻辑。
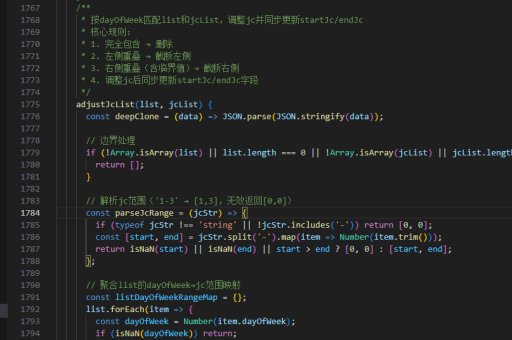
function paginate(data, itemsPerPage, currentPage) {
const startIndex = (currentPage - 1) * itemsPerPage;
return data.slice(startIndex, startIndex + itemsPerPage);
}
// 示例数据
const allData = Array.from({length: 100}, (_, i) => `Item ${i+1}`);
// 使用示例
const pageSize = 10;
const currentPage = 3;
const pageData = paginate(allData, pageSize, currentPage);
console.log(pageData); // 显示第3页的10条数据后端分页(AJAX请求)
适用于大数据量场景,需要与后端API配合。

async function fetchPaginatedData(page, size) {
try {
const response = await fetch(`/api/data?page=${page}&size=${size}`);
const result = await response.json();
return {
data: result.items,
total: result.totalCount
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching data:', error);
return { data: [], total: 0 };
}
}
// 使用示例
const currentPage = 1;
const pageSize = 10;
fetchPaginatedData(currentPage, pageSize)
.then(({data, total}) => {
console.log('Fetched data:', data);
renderPaginationControls(total, pageSize);
});
function renderPaginationControls(totalItems, itemsPerPage) {
const totalPages = Math.ceil(totalItems / itemsPerPage);
// 渲染分页UI逻辑
}完整分页组件实现
包含分页逻辑和UI控制的完整示例:
class Pagination {
constructor({ data = [], pageSize = 10, currentPage = 1 }) {
this.data = data;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.currentPage = currentPage;
this.totalPages = Math.ceil(data.length / pageSize);
}
getPaginatedData() {
const start = (this.currentPage - 1) * this.pageSize;
const end = start + this.pageSize;
return this.data.slice(start, end);
}
nextPage() {
if (this.currentPage < this.totalPages) {
this.currentPage++;
}
return this.getPaginatedData();
}
prevPage() {
if (this.currentPage > 1) {
this.currentPage--;
}
return this.getPaginatedData();
}
goToPage(page) {
if (page >= 1 && page <= this.totalPages) {
this.currentPage = page;
}
return this.getPaginatedData();
}
}
// 使用示例
const paginator = new Pagination({
data: Array.from({length: 50}, (_, i) => `Item ${i+1}`),
pageSize: 5
});
console.log(paginator.getPaginatedData()); // 第1页
console.log(paginator.nextPage()); // 第2页
console.log(paginator.goToPage(3)); // 第3页分页UI渲染
结合DOM操作的分页控件实现:
function renderPagination(data, containerId, itemsPerPage = 10) {
const container = document.getElementById(containerId);
const totalPages = Math.ceil(data.length / itemsPerPage);
let currentPage = 1;
function renderPage(page) {
const start = (page - 1) * itemsPerPage;
const end = start + itemsPerPage;
const pageData = data.slice(start, end);
// 清空容器并渲染当前页数据
container.innerHTML = '';
pageData.forEach(item => {
const div = document.createElement('div');
div.textContent = item;
container.appendChild(div);
});
// 渲染分页控件
renderPaginationControls();
}
function renderPaginationControls() {
const controls = document.createElement('div');
controls.className = 'pagination-controls';
// 上一页按钮
const prevBtn = document.createElement('button');
prevBtn.textContent = 'Previous';
prevBtn.disabled = currentPage === 1;
prevBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
if (currentPage > 1) {
currentPage--;
renderPage(currentPage);
}
});
// 页码按钮
const pages = document.createElement('div');
for (let i = 1; i <= totalPages; i++) {
const pageBtn = document.createElement('button');
pageBtn.textContent = i;
pageBtn.className = i === currentPage ? 'active' : '';
pageBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
currentPage = i;
renderPage(currentPage);
});
pages.appendChild(pageBtn);
}
// 下一页按钮
const nextBtn = document.createElement('button');
nextBtn.textContent = 'Next';
nextBtn.disabled = currentPage === totalPages;
nextBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
if (currentPage < totalPages) {
currentPage++;
renderPage(currentPage);
}
});
controls.appendChild(prevBtn);
controls.appendChild(pages);
controls.appendChild(nextBtn);
container.appendChild(controls);
}
// 初始渲染
renderPage(currentPage);
}
// 使用示例
const testData = Array.from({length: 35}, (_, i) => `Data Item ${i+1}`);
renderPagination(testData, 'data-container', 5);这些实现涵盖了从简单数据分片到完整分页组件的不同场景,可以根据具体需求选择适合的方案或组合使用。