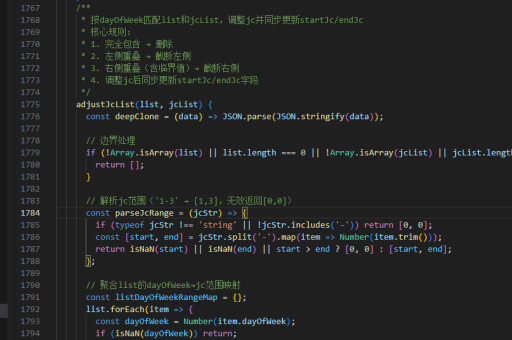
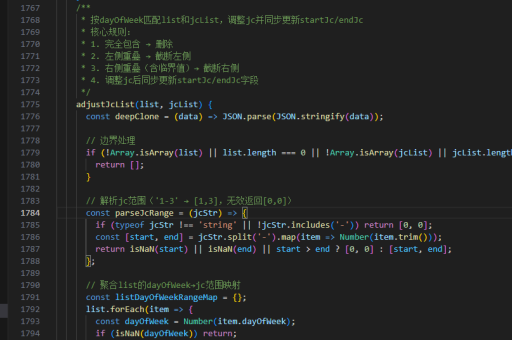
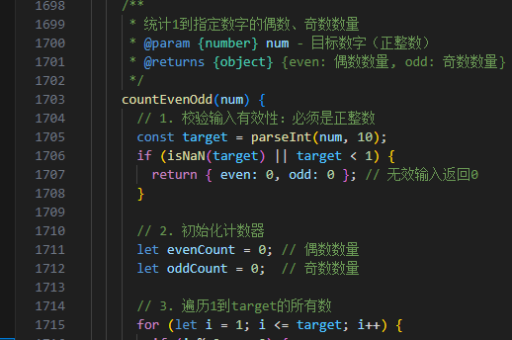
php实现struct
在PHP中,没有内置的struct数据类型(如C语言中的结构体),但可以通过多种方式模拟类似的功能。以下是几种常见的实现方法:
使用关联数组
关联数组可以模拟结构体的键值对存储方式,适合简单场景:
$person = [
'name' => 'John',
'age' => 30,
'email' => 'john@example.com'
];
echo $person['name']; // 输出: John使用stdClass对象
PHP的stdClass是一个空类,可以动态添加属性:

$person = new stdClass();
$person->name = 'John';
$person->age = 30;
echo $person->name; // 输出: John定义自定义类
通过类封装属性和方法,这是最接近传统结构体的实现方式:
class Person {
public $name;
public $age;
public $email;
}
$person = new Person();
$person->name = 'John';
$person->age = 30;
echo $person->name; // 输出: John使用匿名类(PHP 7+)
匿名类适合一次性使用的简单结构:
$person = new class {
public $name;
public $age;
};
$person->name = 'John';
echo $person->name; // 输出: John强类型属性(PHP 7.4+)
PHP 7.4引入的类型属性可以增强结构体的类型安全:
class Person {
public string $name;
public int $age;
}
$person = new Person();
$person->name = 'John';
$person->age = 30;使用数组访问接口
实现ArrayAccess接口使对象能像数组一样操作:
class Struct implements ArrayAccess {
private $data = [];
public function offsetExists($offset): bool {
return isset($this->data[$offset]);
}
public function offsetGet($offset) {
return $this->data[$offset] ?? null;
}
public function offsetSet($offset, $value): void {
$this->data[$offset] = $value;
}
public function offsetUnset($offset): void {
unset($this->data[$offset]);
}
}
$person = new Struct();
$person['name'] = 'John';
echo $person['name']; // 输出: John性能考虑
- 关联数组在读写速度上通常最快
- 自定义类在复杂场景中更易维护
- PHP 7.4+的强类型属性能减少运行时错误
选择哪种方式取决于具体需求,简单数据结构可用数组或stdClass,复杂场景建议使用自定义类。