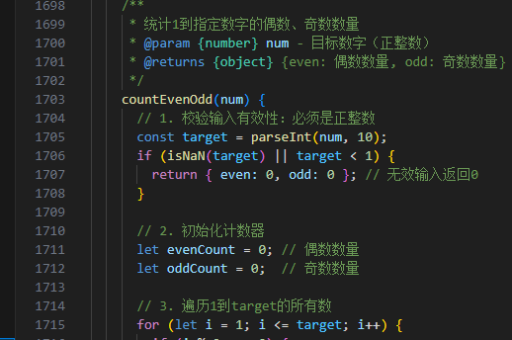
react 如何修改props
在 React 中,props 是只读的,直接修改 props 会违反 React 的设计原则。但可以通过以下方法间接实现类似效果:
使用状态提升
将需要修改的数据提升到父组件中管理,通过回调函数让子组件触发父组件的状态更新。父组件更新后,新的 props 会传递给子组件。
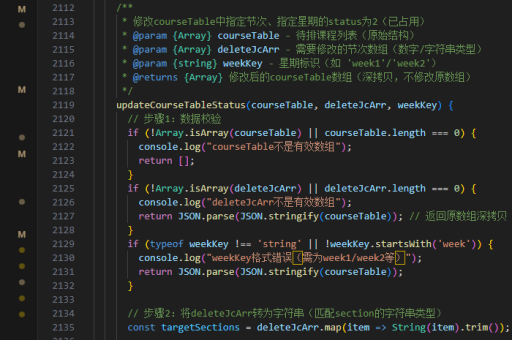
// 父组件
function Parent() {
const [value, setValue] = useState('initial');
const handleChange = (newValue) => {
setValue(newValue);
};
return <Child value={value} onChange={handleChange} />;
}
// 子组件
function Child({ value, onChange }) {
return <input value={value} onChange={(e) => onChange(e.target.value)} />;
}使用状态派生
在子组件内部使用 state 来存储 props 的初始值,后续修改只影响内部状态。适用于需要基于 props 初始化但之后独立控制的场景。

function Child({ initialValue }) {
const [value, setValue] = useState(initialValue);
return <input value={value} onChange={(e) => setValue(e.target.value)} />;
}使用 ref 存储可变值
对于需要在组件间共享且可能变化的值,可以使用 useRef 创建一个可变引用。注意这不会触发重新渲染。
function Child({ initialValue }) {
const valueRef = useRef(initialValue);
const updateValue = (newValue) => {
valueRef.current = newValue;
};
// ...
}使用 Context API
对于深层嵌套组件间的数据共享,可以通过 Context 提供数据和更新函数。
const ValueContext = createContext();
function Parent() {
const [value, setValue] = useState('initial');
return (
<ValueContext.Provider value={{ value, setValue }}>
<Child />
</ValueContext.Provider>
);
}
function Child() {
const { value, setValue } = useContext(ValueContext);
return <input value={value} onChange={(e) => setValue(e.target.value)} />;
}每种方法适用于不同场景,选择取决于组件层级关系和数据流需求。状态提升适合父子组件通信,Context 适合跨层级共享,而状态派生适合需要内部控制的场景。