vue实现逻辑回归分析
在Vue中实现逻辑回归分析通常需要结合前端框架与数学库。以下是具体实现方法:
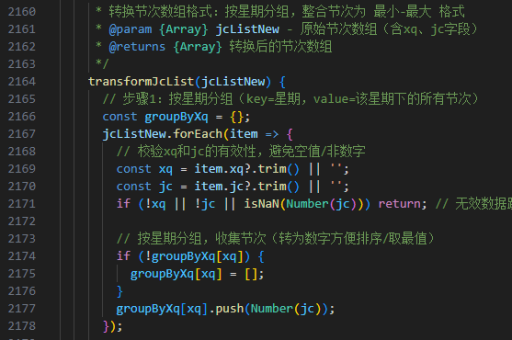
数据准备与预处理
将数据集格式化为适合逻辑回归的数值形式。假设有一个二维数组dataset,包含特征和标签:
data() {
return {
dataset: [
{ features: [1, 2], label: 0 },
{ features: [2, 3], label: 1 },
// 更多数据...
]
}
}引入数学计算库
使用mathjs或tensorflow.js进行矩阵运算。安装后引入:
import * as math from 'mathjs'
// 或
import * as tf from '@tensorflow/tfjs'实现Sigmoid函数
逻辑回归核心函数实现:
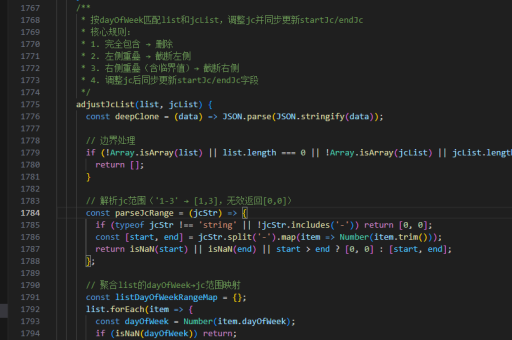
methods: {
sigmoid(z) {
return 1 / (1 + Math.exp(-z))
}
}权重初始化
为特征权重和偏置项设置初始值:
data() {
return {
weights: Array(this.dataset[0].features.length).fill(0),
bias: 0,
learningRate: 0.1
}
}训练过程实现
迭代更新权重参数:

train() {
const epochs = 1000
for (let epoch = 0; epoch < epochs; epoch++) {
let totalLoss = 0
this.dataset.forEach(data => {
const z = math.dot(data.features, this.weights) + this.bias
const prediction = this.sigmoid(z)
const error = prediction - data.label
// 更新权重
this.weights = this.weights.map((w, i) =>
w - this.learningRate * error * data.features[i]
)
this.bias -= this.learningRate * error
totalLoss += -data.label * Math.log(prediction) -
(1 - data.label) * Math.log(1 - prediction)
})
console.log(`Epoch ${epoch}, Loss: ${totalLoss}`)
}
}预测函数
训练完成后进行预测:
predict(features) {
const z = math.dot(features, this.weights) + this.bias
return this.sigmoid(z) > 0.5 ? 1 : 0
}可视化展示
使用图表库展示结果:
import Chart from 'chart.js'
mounted() {
this.train()
this.renderChart()
}
renderChart() {
const ctx = this.$refs.chartCanvas
new Chart(ctx, {
type: 'scatter',
data: {
datasets: [{
data: this.dataset.map(d => ({
x: d.features[0],
y: d.features[1],
backgroundColor: d.label ? 'red' : 'blue'
}))
}]
}
})
}使用TensorFlow.js简化实现
更简洁的实现方式:
async tfTrain() {
const xs = tf.tensor2d(this.dataset.map(d => d.features))
const ys = tf.tensor1d(this.dataset.map(d => d.label))
const model = tf.sequential()
model.add(tf.layers.dense({
units: 1,
inputShape: [this.dataset[0].features.length],
activation: 'sigmoid'
}))
model.compile({
optimizer: tf.train.adam(0.1),
loss: 'binaryCrossentropy'
})
await model.fit(xs, ys, {
epochs: 100,
callbacks: {
onEpochEnd: (epoch, logs) =>
console.log(`Epoch ${epoch}: loss = ${logs.loss}`)
}
})
const test = tf.tensor2d([[1.5, 2.5]])
model.predict(test).print()
}实现时需注意浏览器内存限制,大数据集建议分批次训练。可视化组件建议使用专门的图表库如ECharts或D3.js进行更专业的展示。